This year, there were about 200 students with 69 projects from 9 faculties of HCMUT – Bach Khoa taking part in the 6th Science and Technology Symposium. Symposium had seven sessions that took place on campus 1 at HCMUT – Bach Khoa. Each session consisted of the projects in 2 and 3 faculties. After many tough rounds, 7 projects winning the first size at seven sessions have been revealed.

1. Study on the Motion Control of a Torpedo through the Water
Project team: Nguyen Gia Thinh, Tran Lam Duy from the Faculty of Mechanical Engineering with the support from Dr. Thanh-Long Le at National Key Laboratory of Digital Control and System Engineering (DCSE Lab)
In this study, the proposed algorithm is utilized to optimize the motion control analysis and mathematical model for a torpedo. Torpedo is the popular weapon of submerged fighting, but a successful attack is not achieved easily. This paper gives an illustration about using MATLAB, Simulink,…to calculate the equations of motion and math functions for controlling propeller with tail wings, rudders and finding the best way to achieve the desired value. To optimize the system, a Micro-Electro-Mechanical System (MEMS) Gyroscope and Proportional Integral Derivative (PID) controller are essential. An emulated MEMS Gyroscope is adjusted and simulated so that its simulated result matches with the practical MEMS Gyroscope. The PID controller is used to obtain better control performance over the motion. The numerical results show the response of the control system and the controller performance are stable and accurate. A comparison of the system performance between a torpedo with and without PID controller is also investigated.
2. Numerical modeling of multiphase flow in the oil and gas gathering pipeline from the wellhead platform of oilfield X to the central processing platform of oilfield Y
Project team: Nguyen Hoai Tan and Mai Cao Lan from the Faculty of Geology and Petroleum
The main objective of this research is to investigate the characteristics of the slug flow inside the riser which is a 68-meter vertical pipe segment reaching from the seabed to the central processing platform (CPP) of oilfield Y. The oil and gas mixture flows into the riser from the wellhead platform (WHP) of oilfield X through a 25-km horizontal pipeline. Starting from the numerical modeling of oil and gas behavior and multiphase flow in the gathering pipeline, we have constructed a slug-tracking model to characterize the slug flow of oil and gas mixture with essential properties such as slug frequency, length and surge volume. The results from this integrated modeling approach can help identify slug flow existence inside the pipeline, especially in the riser and estimate potential consequences it may cause to surface facilities on the CPP.
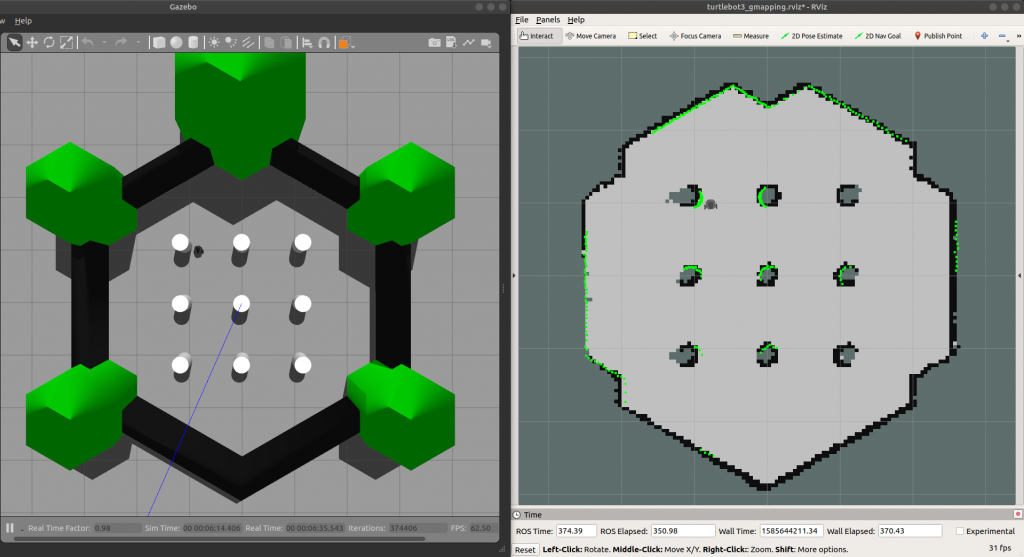
3. Study and implement SLAM algorithm in autonomous mobile robot
Project team: Duc-Tuan Ngo, Khoa L.V. Truong, Quyen L. T. Ho, and Hoang-Anh Pham from the Faculty of Computer Science and Engineering
Simultaneous Localization And Mapping (SLAM) is the process of estimating the location of a mobile robot concurrently with constructing a model (the map) of the surrounding environment. The SLAM community has made breathtaking progress over the last two decades, varying from indoor mobile robot navigation to large-scale real-world applications. In this study, we develop a prototype of a mobile robot deployed conventional sensors (e.g., IMU, 2D Lidar, 3D camera) to investigate compatibility and performance of several SLAM implementations that are compatible with Robot Operating System (ROS) such as Gmapping, Hector Slam and Cartographer. Our SLAM implementation is imported on NVidia Jetson TX2 as a part of the self-driving process in navigation task and object detection/avoidance.
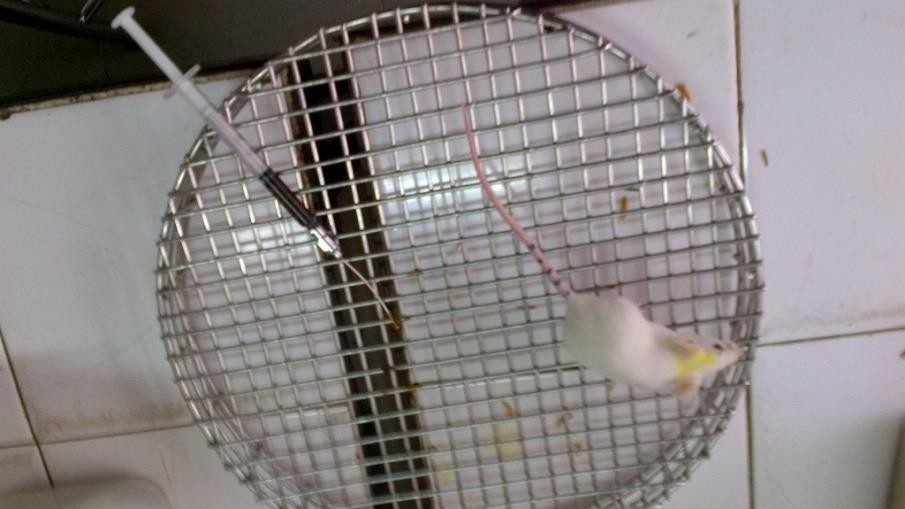
4. Extracting Crotalaria assamica Benth seeds, inspecting the antioxidant and antibacterial activity, and analyzing some basic ingredients of the product
Project team: Nguyen Long Hoang, Le Thao Hien, Vo Viet Tien, Nguyen Dinh Quan, Tran Thi Ngoc Yen from the Faculty of Chemical Engineering, Faculty of Pharmacy.
Crotalaria assamica Benth, which belongs to Fabaceae family, is a commonly available herb in Asian countries, such as China, Vietnam, Japan, etc. Most of the studies on its toxicity and anti-inflammatory activity have been carried out on in vitro models. In this study, crude extract from dark roasting and the land cooling seed of Crotalaria assamica Benth was investigated and tested on in vivo models with ultrasound extraction in 90 wt. % ethanol. Alkaloid, coumarin, flavonoid, tannin, and saponin compounds were detected by I.Ciulei qualitative analysis method, among which alkaloids and flavonoids were found with the strongest positive signs. Sequentially, the crude extract was tested for antioxidant capacity, antibacterial activity, and acute toxicity. To elucidate the safety of using this herb as botanical medicine, its acute toxicity was tested on mice. A feeding dose of 0.2 mL crude extract/10 g weight of mice was safe for the mice during the 14-day-test.


5. Optimizing nanosuspension preparation from cinnamon extract
Project team: Bui Minh Dang, Le Thi Hong Nhan from the Faculty of Chemical Engineering
Cinnamon cassia has abilities to adapt all the relevant requirements on biological and pharmaceutical benefits. However, in the crude form of cinnamon, the solubility of this plant as well as its chemical constituents has been limited, which leads to its shortcoming in digestive products. Therefore, nano dispersion co-operated with surfactants emerged with outstanding advantages, enhancing solubility of cinnamon as well as improving the biological and pharmaceutical abilities through digestion. The aims of this study are preparing nanosuspension, investigating and optimizing preparation cinnamon suspensions. Results of optimized factors for the response median size contains ratio between cinnamon extract: lecithin was 1:1.0520924, homogenization speed was 6602.9007 rpm, homogenization time was 46.581269 minutes. The variance analysis showed that all of three factors had a considerable effect on the size of cinnamon suspension. The determination coefficient (R2 of 0.94) and RSME value was 0.2032 as well as the p-value of the model was 0.0054 < 0.05 revealed a good fitting quality. It demonstrated that a suitable condition for factors affecting the preparation of cinnamon suspension was determined. In addition, The Actual by Predicted Plot showed that the model is significant. There was no evidence of lack of fit.
6. Cosmetic product using hydrating agents and evaluating effectiveness
Project team: Hoang Thi Bich Ngoc, Le Thi Hong Nhan from the Faculty of Chemical Engineering
The objective of this topic is to evaluate and compare specifically the moisturizing effect of high molecular weight Hyaluronic Acid and low molecular weight Hyaluronic Acid on serum base. Besides, the topic will be an important basis to help customers make appropriate decisions about the choice of ingredients for moisturizing cosmetic products. All materials used in this project are provided by Asia Shine Co., Ltd. and DKSH Vietnam. Four different polymers were selected for sensory, viscosity and color surveys: SepimaxTM Zen (INCI: Polyacrylate Crosspolymer-6), SolagumTM AX (INCI: Acacia Senegal Gum & Xanthan Gum), SolagumTM Tara (INCI: Caesalpinia Spinosa Gum), SepinovTM EMT10 (Hydroxyethyl Acrylate / Sodium Acryloyldimethyl Taurate Copolymer). Survey results show that SepimaxTM Zen 0.3% gives the most suitable serum base so SepimaxTM Zen 0.3% was selected as the main thickener to formulate moisturizing cosmetic formulas. Serum was chosen as the cosmetic base to evaluate the effectiveness of two types of HA with 4 samples: 0.2% Sodium Hyaluronate 1.79MDa, 0.2% Sodium Hyaluronate 9.78KDa, 0.1% Sodium Hyaluronate 1.79MDa + 0.1% Sodium Hyaluronate 9.78KDa and blank sample. The survey time is limited, so it is not possible to directly evaluate the effectiveness of the product on the skin of volunteers. Therefore, the topic needs to be further studied to investigate the effectiveness as well as the commercialization of products on the market. However, this is the foundation for the research and development of other products as well as other active ingredients.
7. Combination of voice recognition and language model for an intelligent chatbot
Project team: Tran Ngoc Minh Thu, Tran Duc Thinh, Nguyen Duc Huy, Pham Minh Hieu, Cao Chanh Duong, Quan Thanh Tho from the Faculty of Computer Science and Engineering
The speech to text problem is not uncommon, since automatic speech recognition (ASR) is an important feature in a world that is witnessing the rapid development in technology and the evolution of Artificial Intelligence. This problem is getting more and more attention, as its application can be applied in many aspects of modern life, such as human-car automotive interaction, subtitles in movies, clips, virtual assistants,… Chatbots are one of the most advanced interactions between human and machines. A chatbot is a software, with the help of Artificial Intelligence, which can simulate a conversation with a user in natural language, normally through messages. This paper is about combining an end-to-end automatic speech recognition using voice recognition and language model, with an intelligent chatbot, in order to improve and enhance the user experience when using chat applications to ask for services.
These researches are funded by the Office for International Study Programs (OISP), Ho Chi Minh City University of Technology (HCMUT – Bach Khoa), VNU-HCM. We acknowledge the support of time and facilities from HCMUT – Bach Khoa, VNU-HCM for these studies.



